Selenium是一个用于Web应用程序测试的工具。Selenium测试直接运行在浏览器中,就像真正的用户在操作一样。 支持的浏览器包括IE(7, 8, 9, 10, 11),Mozilla Firefox,Safari,Google Chrome,Opera等。 这个工具的主要功能包括:测试与浏览器的兼容性——测试你的应用程序看是否能够很好得工作在不同浏览器和操作系统之上。 测试系统功能——创建回归测试检验软件功能和用户需求。支持自动录制动作和自动生成 .Net、Java、Perl等不同语言的测试脚本。
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>3.14.0</version>
</dependency>2
3
4
5
compile group: 'org.seleniumhq.selenium', name: 'selenium-java', version: '3.14.0'元素定位
有如下一段html,现在要模拟点击搜索按钮
<button id="searchButton" aria-label="Google Search" name="btnK" class="gbqfba">
<span id="gbqfsa">Google Search</span>
</button>2
3
1.By.name()
通过dom元素的name属性定位元素
driver.findElement(By.name("btnK")).click();2.By.id()
通过dom元素的id属性定位元素
driver.findElement(By.id("searchButton")).click();3.By.tagName()
该方法可以通过元素的标签名称来查找元素。该方法跟之前两个方法的区别是,这个方法搜索到的元素通常不止一个,所以一般建议结合使用findElements方法来使用。比如我们现在要查找页面上有多少个button,就可以用button这个tagName来进行查找,代码如下
List<WebElement> buttons = driver.findElements(By.tagName("button"));
//打印出button的个数
System.out.println(buttons.size());
buttons.get(0).click();2
3
4
4.By.className()
className属性是利用元素的css样式表所引用的伪类名称来进行元素查找的方法。对于任何HTML页面的元素来说,一般程序员或页面设计师会给元素直接赋予一个样式属性或者利用css文件里的伪类来定义元素样式,使元素在页面上显示时能够更加美观。
driver.findElement(By.className("buttonStyle")).click();5.By.linkText()
这个方法比较直接,即通过超文本链接上的文字信息来定位元素,这种方式一般专门用于定位页面上的超文本链接。
driver.findElement(By.linkText("About Google")).click();6.By.partialLinkText()
这个方法是上一个方法的扩展。当你不能准确知道超链接上的文本信息或者只想通过一些关键字进行匹配时,可以使用这个方法来通过部分链接文字进行匹配。
driver.findElement(By.partialLinkText("About Google")).click();7.By.xpath()
这个方法是非常强大的元素查找方式,使用这种方法几乎可以定位到页面上的任意元素。在正式开始使用XPath进行定位前,我们先了解下什么是XPath。XPath是XML Path的简称,由于HTML文档本身就是一个标准的XML页面,所以我们可以使用XPath的语法来定位页面元素。
// 查询表单J_login_form下id为J_password的密码框
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='J_login_form']/dl/dt/input[@id='J_password']"));
// 上面示例也可以写为
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='J_login_form']/*/*/input[@id='J_password']"));
// 使用contains方法
// 包含logout的a标签
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//a[contains(@href, 'logout')]"));
// 使用start-with方法
// 以logo开始的a标签
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//a[start-with(@href, 'logo')]"));
// 按照文字匹配text
// 文本为退出的元素
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[text()='退出']"));
// 选取元素之前的元素 preceding-sibling
// 选取元素之后的元素 following-sibling
// 选取id为button的元素之前的a标签
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id=\"button\"]/preceding-sibling::a"));2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
8.By.cssSelector()
cssSelector这种元素定位方式跟xpath比较类似,但执行速度较快,而且各种浏览器对它的支持都相当到位,所以功能也是蛮强大的。 下面是一些常见的cssSelector的定位方式: 定位id为flrs的div元素,可以写成:#flrs 注:相当于xpath语法的//div[@id='flrs'] 定位id为flrs下的a元素,可以写成 #flrs > a 注:相当于xpath语法的//div[@id='flrs']/a 定位id为flrs下的href属性值为/forexample/about.html的元素,可以写成: #flrs > a[href="/forexample/about.html"]
// 选取id为J_login_form的表单dl>dt元素下id为J_password的input元素
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("#J_login_form>dl>dt>input[id='J_password']"));
// 选取button class为btn btn_big btn_submit的元素
driver.findElement(By.cssSelector("button.btn.btn_big.btn_submit"))2
3
4
Java代码
1.驱动下载
选择对应客户端浏览器版本的Chrome驱动
2.驱动配置
@Configuration
public class WebDriverConfig {
@Bean(destroyMethod = "quit")
public WebDriver webDriver() throws IOException {
// 设置驱动位置
System.setProperty(
"webdriver.chrome.driver",
new ClassPathResource("/driver/chrome/chromedriver.exe").getFile().getAbsolutePath()
);
// Chrome选项
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
//--user-agent="" 设置请求头的User-Agent
//--window-size=1366,768 设置浏览器分辨率(窗口大小)
//--headless 无界面运行(无窗口)
//--start-maximized 最大化运行(全屏窗口)
//--incognito 隐身模式(无痕模式)
//--disable-javascript 禁用javascript
//--disable-infobars 禁用浏览器正在被自动化程序控制的提示
// 无痕模式 最大化
options.addArguments("--incognito", "--start-maximized");
return new ChromeDriver(options);
}
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
3.编写测试脚本
考虑为web系统,所有功能都会涉及登录,把登录提取到父类中
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class BaseSpec {
/**
* 浏览器驱动
*/
@Autowired
protected WebDriver webDriver;
/**
* 测试目标地址
*/
@Value("${selenium.targetHost}")
String targetHost;
/**
* 测试系统默认用户
*/
@Value("${selenium.defaultUserName}")
String defaultUserName;
/**
* 测试系统默认密码
*/
@Value("${selenium.defaultUserPassword}")
String defaultUserPassword;
/**
* 默认交互等待时间(秒)
*/
@Value("${selenium.waitSeconds}")
int waitSeconds;
@PostConstruct
public void setUp() {
this.webDriver.get(this.targetHost);
this.sleep(1);
}
/**
* 默认管理员登录
*/
protected void login() {
this.login(this.defaultUserName, this.defaultUserPassword);
}
/**
* 指定用户名密码登录
* @param loginName 用户名
* @param password 密码
*/
@SneakyThrows
protected void login(String loginName, String password) {
this.sleep(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 500);
this.webDriver.findElement(By.id("userName")).sendKeys(loginName);
this.webDriver.findElement(By.id("passWord")).sendKeys(password);
this.webDriver.findElement(By.className("submit-btn")).click();
this.sleep();
}
/**
* 等待默认时间
*/
protected void sleep() {
this.sleep(this.waitSeconds);
}
/**
* 等待
* @param seconds 等待秒数
*/
protected void sleep(int seconds) {
this.sleep(TimeUnit.SECONDS, seconds);
}
@SneakyThrows
protected void sleep(TimeUnit timeUnit, int time) {
timeUnit.sleep(time);
}
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
4.自动化登录测试
public class StudentRegisterSpec extends BaseSpec {
@Test
public void login() {
// 登录
super.login();
}
}2
3
4
5
6
7
5.其他
其他业务测试可以通过扩展BaseSpec进行业务测试
6.登录自动测试示例
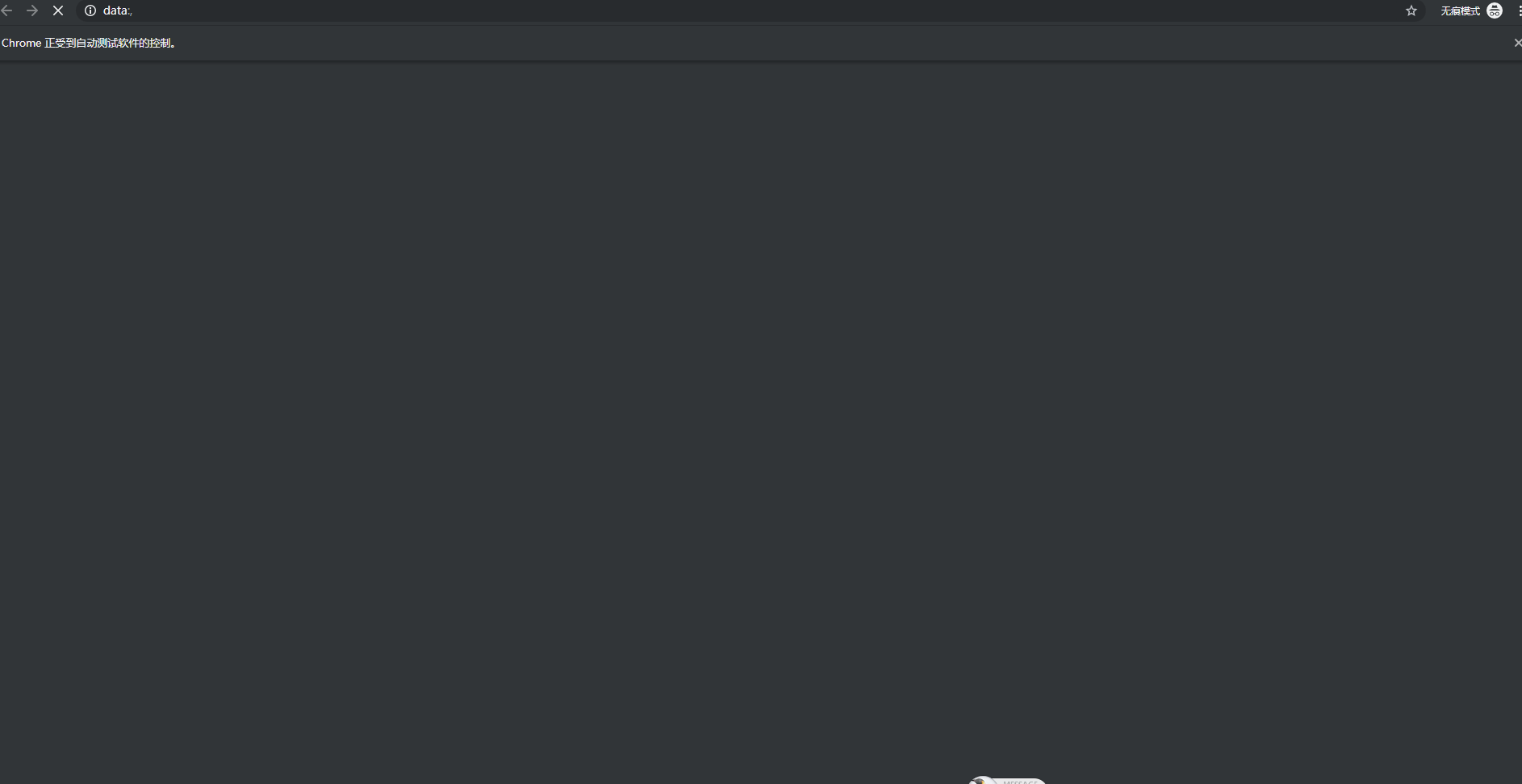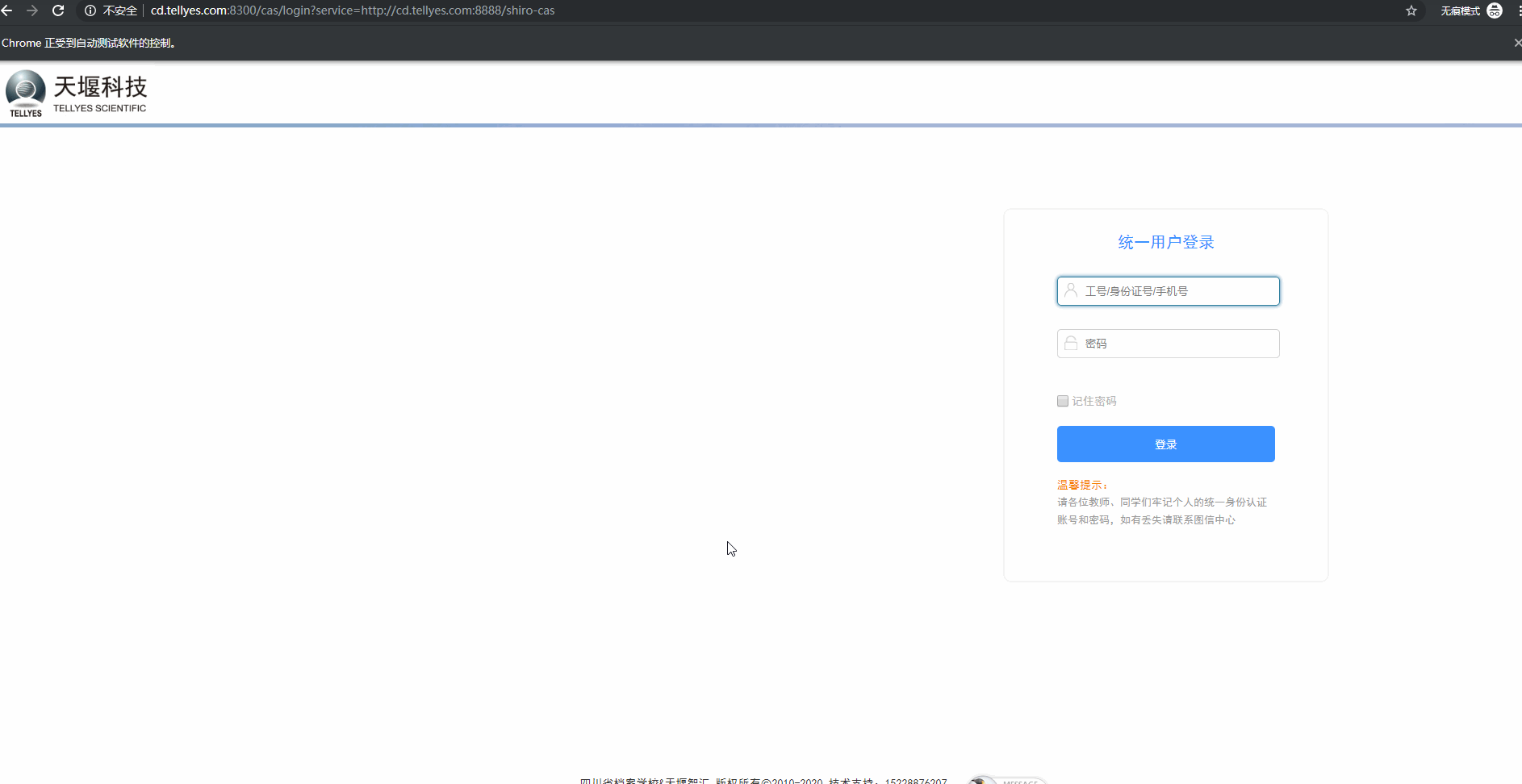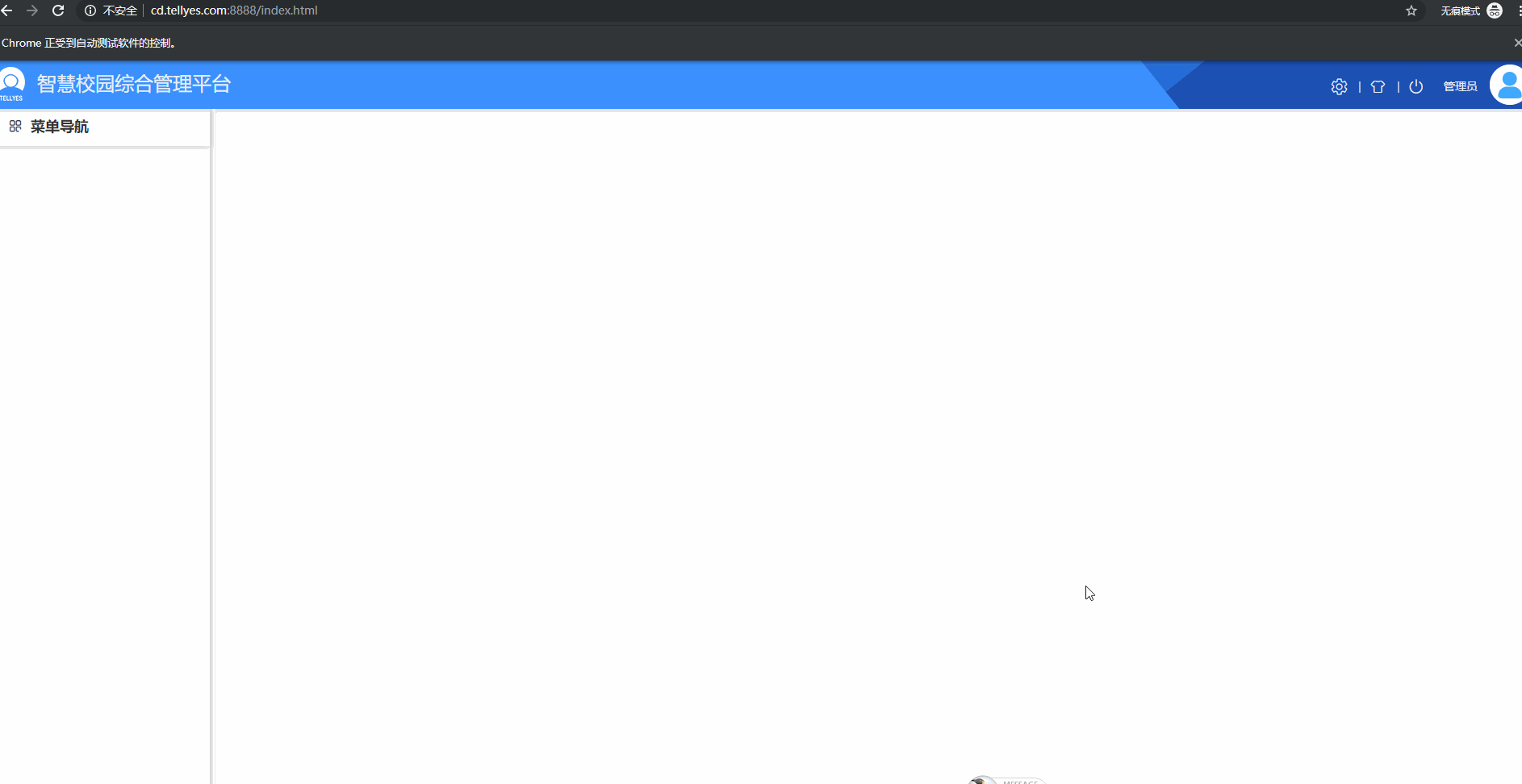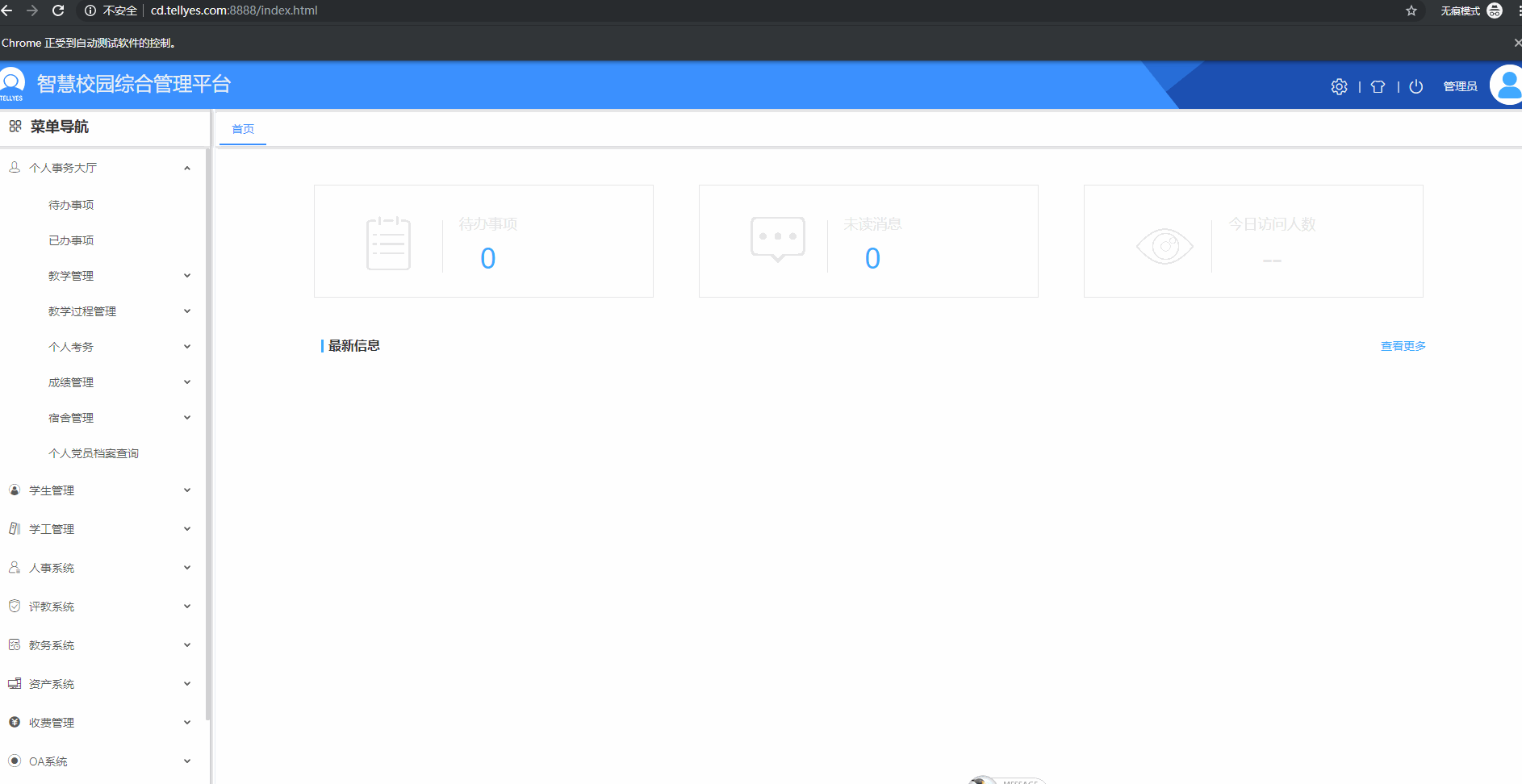
结论
需要在系统比较稳定的时候用于自动回归测试,会产生数据,需要准备一个纯净环境专门用于自动化测试。